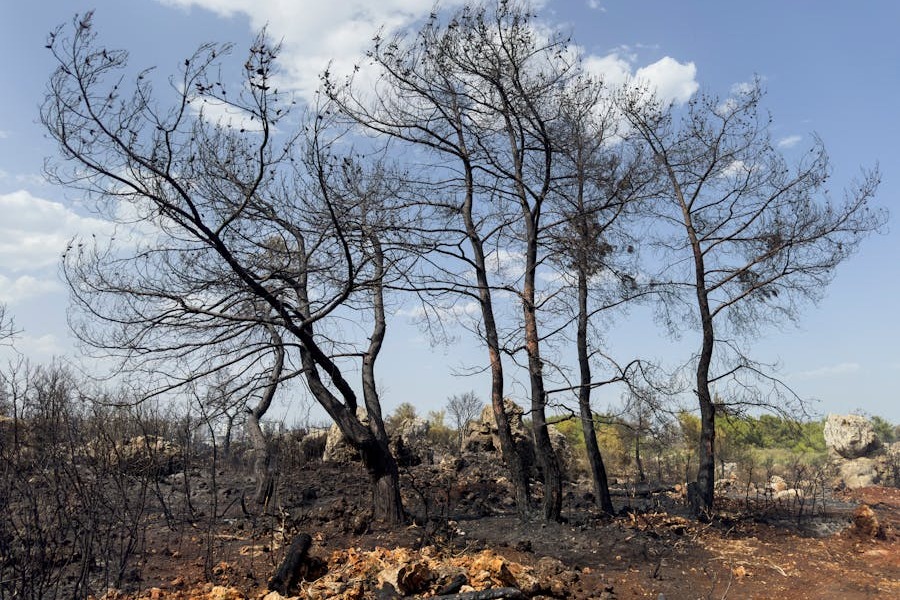
South Africa, known for its diverse ecosystems and rich natural resources, is increasingly vulnerable to climate change. Over the past few decades, the country has experienced rising temperatures, erratic weather patterns, and increased droughts. These changes threaten its biodiversity, economic stability, and food security. Understanding the causes of climate change in South Africa is essential for developing strategies to mitigate its effects and ensure sustainable development.
The primary drivers of climate change in South Africa include greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and industrial activities. Coupled with global influences, these local factors exacerbate the already fragile ecological balance. Additionally, the country’s reliance on coal-fired power plants and unsustainable agricultural practices further contributes to the problem.
This detailed article will explore the root causes of climate change in South Africa, discuss their environmental and social impacts, and provide actionable insights on addressing these challenges. Whether you’re a policymaker, environmental enthusiast, or concerned citizen, this guide offers a comprehensive understanding of the issue and potential solutions.
Causes of Climate Change in South Africa
The causes of climate change in South Africa include greenhouse gas emissions from coal power plants, deforestation, industrial pollution, and unsustainable agricultural practices. These factors lead to rising temperatures, erratic rainfall, and increased droughts, threatening the country’s biodiversity and economy. Tackling these challenges requires a shift toward renewable energy, reforestation, and sustainable farming practices.
Why Climate Change is a Critical Issue in South Africa
South Africa’s unique geographical location and reliance on natural resources make it particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. With an economy heavily dependent on mining, agriculture, and energy production, the environmental consequences of climate change are deeply intertwined with social and economic challenges.
One of the key concerns is the country’s water scarcity. Over 80% of South Africa’s land is classified as arid or semi-arid, making water a critical resource for both human consumption and agricultural activities. Climate change intensifies water scarcity by reducing rainfall and increasing evaporation rates. This threatens food production and exacerbates inequalities in access to clean water.
Furthermore, rising temperatures have far-reaching impacts on biodiversity. South Africa is home to some of the world’s most diverse ecosystems, including savannahs, forests, and marine environments. Changes in temperature and precipitation disrupt these ecosystems, leading to habitat loss and the extinction of vulnerable species.
The economic impact of climate change is equally alarming. Industries like agriculture and tourism, which rely heavily on stable weather patterns, face significant risks. For instance, droughts reduce crop yields, while rising sea levels threaten coastal infrastructure and tourism hotspots. Understanding and addressing the causes of climate change in South Africa is a matter of urgency for both environmental and economic sustainability.
The Key Causes of Climate Change in South Africa
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
South Africa is one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases in Africa, primarily due to its reliance on coal-fired power plants. Coal accounts for over 70% of the country’s energy production, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. This contributes to global warming and exacerbates climate change.
Deforestation and Land Use Changes
Deforestation for agriculture, urbanization, and mining activities significantly impacts South Africa’s carbon sequestration capacity. Forests act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Their removal releases stored carbon and reduces the land’s ability to capture future emissions.
Industrial Pollution
The industrial sector in South Africa contributes to air and water pollution, releasing methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O), potent greenhouse gases. Factories, chemical plants, and mining operations emit pollutants that harm the environment and human health.
Agricultural Practices
Agriculture in South Africa, particularly livestock farming, produces significant methane emissions. Unsustainable practices like overgrazing and excessive chemical fertilizers degrade soil quality, reduce carbon storage capacity, and release additional greenhouse gases.
Urbanization and Transport
Rapid urbanization has increased energy consumption, waste generation, and vehicle emissions. South Africa’s cities, with their growing populations, contribute to rising CO2 levels, further intensifying climate change.
How These Factors Impact South Africa’s Environment and Society?
- Rising Temperatures: Increased greenhouse gases result in higher average temperatures, which affect agricultural productivity and increase the risk of wildfires.
- Erratic Rainfall: Irregular rainfall patterns lead to droughts in some areas and floods in others, disrupting ecosystems and livelihoods.
- Water Scarcity: Reduced rainfall and over-extraction of groundwater exacerbate water shortages, particularly in regions like the Western Cape.
- Biodiversity Loss: Habitat destruction and changing climate conditions threaten iconic species like rhinos and elephants.
- Economic Challenges: Climate change disrupts industries like agriculture and tourism, leading to job losses and economic instability.
Solutions to Mitigate Climate Change in South Africa
Addressing the causes of climate change in South Africa requires a multi-faceted approach involving government policies, community action, and technological innovation.
Transition to Renewable Energy
Shifting from coal to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower is critical. Given its high levels of sunlight, South Africa has significant potential for solar energy. Government incentives and investments in renewable energy projects can accelerate this transition.
Reforestation and Conservation
Protecting existing forests and implementing reforestation programs can enhance carbon sequestration. Community-driven conservation projects and partnerships with NGOs can amplify these efforts.
Sustainable Agriculture
Encouraging sustainable farming practices, such as crop rotation, organic farming, and water-efficient irrigation, can reduce the agricultural sector’s carbon footprint. Supporting small-scale farmers through training and subsidies is also essential.
Policy and Legislation
Strengthening environmental regulations and enforcing penalties for industrial pollution can drive compliance. Policies promoting sustainable urban planning and public transportation can reduce emissions from urbanization.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about climate change and promoting eco-friendly practices among individuals and businesses can lead to collective action. Educational campaigns and school programs play a crucial role in shaping future generations.
The Role of Individuals in Combating Climate Change
Individual actions, though seemingly small, can collectively make a significant difference. From reducing energy consumption at home to supporting sustainable products, every effort counts. Simple practices like recycling, using energy-efficient appliances, and reducing single-use plastics can contribute to a greener South Africa.
Furthermore, individuals can advocate for change by supporting environmental policies, participating in community clean-up drives, and investing in renewable energy solutions for personal use. The power of collective action must be considered when addressing the causes of climate change in South Africa.
Bottom Line
The causes of climate change in South Africa are deeply rooted in human activity, from greenhouse gas emissions to deforestation and industrial pollution. Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated effort across all sectors of society, including government, businesses, and individuals. By transitioning to renewable energy, adopting sustainable practices, and raising public awareness, South Africa can mitigate the impacts of climate change and safeguard its environment for future generations.
This fight against climate change is not just about protecting ecosystems; it’s about securing water resources, food security, and economic stability. Today’s choices will determine the country’s resilience and prosperity in a changing climate.
FAQ’s
Q: What are the main causes of climate change in South Africa?
A: The main causes include greenhouse gas emissions from coal power plants, deforestation, industrial pollution, unsustainable agriculture, and urbanization.
Q: How does climate change affect South Africa’s biodiversity?
A: Climate change disrupts ecosystems, leading to habitat loss and threatening the extinction of species like rhinos and elephants.
Q: What is South Africa doing to combat climate change?
A: To address climate change, the country is transitioning to renewable energy, implementing conservation programs, and promoting sustainable agriculture.
Q: How can individuals contribute to reducing climate change in South Africa?
A: Individuals can reduce energy consumption, recycle, support eco-friendly policies, and adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives.
Q: Why is renewable energy important for South Africa?
A: Renewable energy reduces reliance on coal, decreases greenhouse gas emissions, and ensures a sustainable and cleaner future.