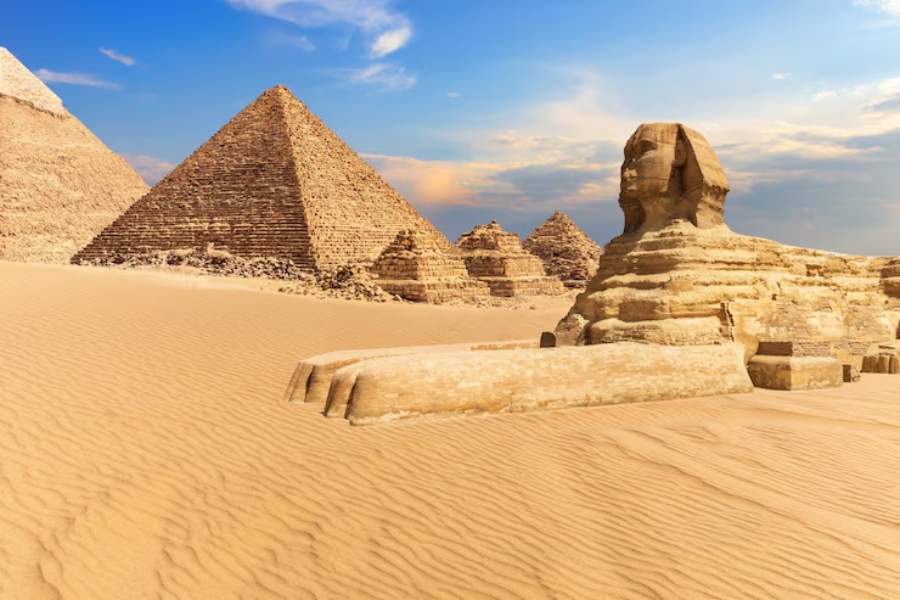
Have you ever wondered why the Nile was called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt? This mighty river wasn’t just a geographical landmark but the foundation of a thriving civilization. Its annual floods transformed barren deserts into fertile fields, sustaining agriculture, trade, and cultural development. The Nile’s influence reached every aspect of life, from the gods of Egyptian mythology to bustling trade routes and monumental structures. This article explores why the Nile was called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt, revealing how its waters nurtured communities, fostered economic prosperity, and shaped a vibrant cultural identity. Join us on this journey through history to uncover how one river became the driving force behind the remarkable achievements of an ancient empire. Let’s dive in and discover the secrets of Egypt’s lifeblood!
Why was the Nile called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt?
The Nile was called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt because it sustained agriculture, provided essential resources, and enabled trade. Its annual floods enriched the soil, while its waters facilitated transportation and cultural exchange, making it vital to Egypt’s civilization.
The Nile’s Agricultural Impact That Fed a Civilization
The Nile’s annual floods were the lifeline of ancient Egypt, transforming the otherwise arid and desolate desert into fertile, productive farmland. These predictable floods deposited rich, nutrient-laden silt onto the riverbanks, making the soil ideal for growing staple crops such as wheat, barley, and flax. This agricultural abundance was more than just sustenance; it laid the foundation for Egypt’s economy, enabling the production of food surpluses that could be stored or traded, fueling commerce and the growth of cities. The river’s consistent flooding cycles were so reliable that they shaped the ancient Egyptian calendar, allowing farmers to plan their planting and harvest seasons precisely.
This predictability fostered stability and prosperity, supporting the population and enabling the construction of monumental architecture. The pharaohs capitalized on these agricultural riches to strengthen their rule, using grain stores to control the economy and reward loyal subjects. Without the Nile’s generosity, Egypt’s transformation into one of history’s most remarkable civilizations might never have occurred. Understanding why the Nile was called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt reveals how this river sustained an empire and shaped its destiny.
How the Nile Shaped Ancient Egyptian Culture and Spirituality
The Nile was not just a river—it was the soul of ancient Egyptian culture, shaping their mythology, rituals, and artistic expression. Understanding why the Nile was called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt requires exploring how deeply it influenced their daily lives and beliefs.
The River in Egyptian Mythology
Ancient Egyptians revered the Nile as a divine and life-giving force, believing it to be the gift of the gods. Personified by the deity Hapi, the river was worshipped as the bringer of fertility and sustenance through its annual floods. These life-giving waters were seen as a direct blessing from Hapi, ensuring the prosperity and survival of the civilization that thrived along its banks.
Temples and Rituals Along the Nile
Temples constructed along the riverbanks stood as symbols of gratitude and devotion to the gods believed to control the Nile’s bounty. Priests performed elaborate rituals and offerings to honor deities like Hapi and Osiris, ensuring the floods would return year after year. These ceremonies were central to maintaining harmony between nature and society.
Art and Literature Reflecting the Nile
The Nile’s importance permeated every aspect of ancient Egyptian art and literature. Wall paintings, sculptures, and hieroglyphic texts celebrated the river’s generosity and the cycles of planting and harvest. These artistic expressions reinforced the Nile’s role as the heart of Egypt’s culture and daily life.
Festivals and Celebrations
Annual festivals marked the Nile’s flooding, symbolizing rebirth, abundance, and the promise of a new year. These vibrant celebrations brought communities together, reinforcing the cultural and spiritual significance of the river’s gifts and its status as the lifeblood of ancient Egypt.
The Nile’s Economic and Trade Benefits
The Nile’s predictable and navigable routes transformed ancient Egypt into an economic powerhouse. Its natural course acted as a thoroughfare, seamlessly connecting different regions and promoting trade, culture, and prosperity. Here’s how the Nile’s economic impact unfolded:
- Trade Hub: Cities that flourished along the Nile’s banks became vibrant trade centers. Goods were exchanged not only within Egypt but also with neighboring regions like Nubia, the Levant, and further afield.
- Marketplaces: The banks of the Nile bustled with activity as farmers, artisans, and merchants gathered to sell their products. Items like grain, papyrus, and pottery went through these lively markets, fueling economic growth.
- Transportation: The Nile served as an efficient and reliable waterway, enabling the movement of people, goods, and resources throughout the kingdom. This transportation network reduced travel time and connected Egypt’s heartland with distant territories.
- Wealth Accumulation: Trade along the Nile brought wealth that financed monumental architecture, temples, and mighty armies. Prosperity from commerce allowed Egypt to expand and thrive.
- Cultural Exchange: As traders navigated the river, they introduced new ideas, innovations, and technologies—this cultural exchange enriched Egyptian society, strengthening its position as a hub of ancient civilization.
Technological and Scientific Advancements Driven by the Nile
The Nile’s annual floods nourished the land and demanded innovative solutions to manage its mighty waters. Ancient Egyptians rose to the challenge by building sophisticated canals, dikes, and irrigation systems that channeled water across the farmland, ensuring reliable harvests even during dry periods. Predicting the Nile’s floods became a scientific endeavor, with priests using astronomical observations to create calendars that guided planting and religious ceremonies. This focus on celestial movements laid the groundwork for advancements in astronomy and mathematics.
The need to measure and divide fields after each flood also spurred developments in geometry, which would later influence architecture and engineering. The challenges posed by the river’s floods thus turned into opportunities for technological growth, transforming Egypt into a center of innovation and learning. The Nile’s influence on science and technology is a testament to why it was called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt.
The Nile’s Enduring Legacy – A Lifeline Across Time
Exploring why the Nile was called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt reveals its continued relevance today. This legacy endures through Egypt’s dependence on the river for agriculture, culture, and progress.
- The Nile’s Role in Modern Egypt: The Nile continues to be Egypt’s lifeline, sustaining agriculture, providing essential water resources, and generating hydroelectric power that supports modern infrastructure. Its annual flow nurtures fields of wheat and other crops, feeding millions and anchoring Egypt’s economy. The river’s enduring presence underscores why it was historically considered the lifeblood of ancient Egypt, proving that its legacy still pulses through the nation’s heart today.
- The Global Significance of the Nile: The Nile’s influence extends beyond Egypt’s borders. It is a testament to how a single natural resource can shape entire civilizations, leaving an indelible mark on human history. From the rise of ancient Egypt to modern geopolitical negotiations over water rights, the Nile has long been a symbol of life, power, and unity. Its waters connect cultures, foster trade, and support biodiversity, making it one of the world’s most influential rivers.
- Lessons from the Past: Reflecting on why the Nile was called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt reveals lessons in resilience, innovation, and the complex relationship between humans and the environment. Understanding how ancient Egyptians adapted to the river’s cycles inspires us to manage natural resources wisely today. The Nile’s legacy is a reminder that sustainable stewardship can turn nature’s challenges into opportunities for progress and prosperity.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, why the Nile was called the lifeblood of ancient Egypt opens a window into how geography, culture, and human ingenuity shaped one of history’s most enduring civilizations. The Nile was not just a river—it was the lifeline that powered Egypt’s economy, guided its spiritual beliefs, and sustained its people. Its annual floods turned barren land into fertile fields, supporting agriculture and trade that built cities and empires.
Without the Nile’s consistent flow, Egypt’s greatness might have faded into the desert sands, leaving behind only ruins rather than a civilization that still fascinates today’s world. This river truly was the beating heart of ancient Egypt, connecting its past, present, and future.
FAQ’s
Why did the Nile flood every year?
The Nile’s floods were caused by seasonal rains in the Ethiopian highlands. The rains sent water rushing northward, enriching the soil with nutrients essential for agriculture and sustaining Egypt’s economy.
What crops did the Nile support?
Thanks to the river’s fertile banks, ancient Egyptians grew wheat, barley, flax, and vegetables, supporting daily sustenance and trade that helped their civilization thrive.
How did the Nile influence trade?
The river connected Egypt with Africa and the Mediterranean, enabling a steady flow of goods, ideas, and cultural exchange that made trade easy and highly profitable.
Did the Nile have religious significance?
Yes! The Nile was worshipped as a divine entity, and many religious rituals, festivals, and myths were tied to its cycles, reinforcing its sacred status in Egyptian culture.
Is the Nile still important today?
Absolutely. The Nile remains Egypt’s primary water source, vital for agriculture, drinking water, and energy, ensuring the nation’s survival and prosperity.