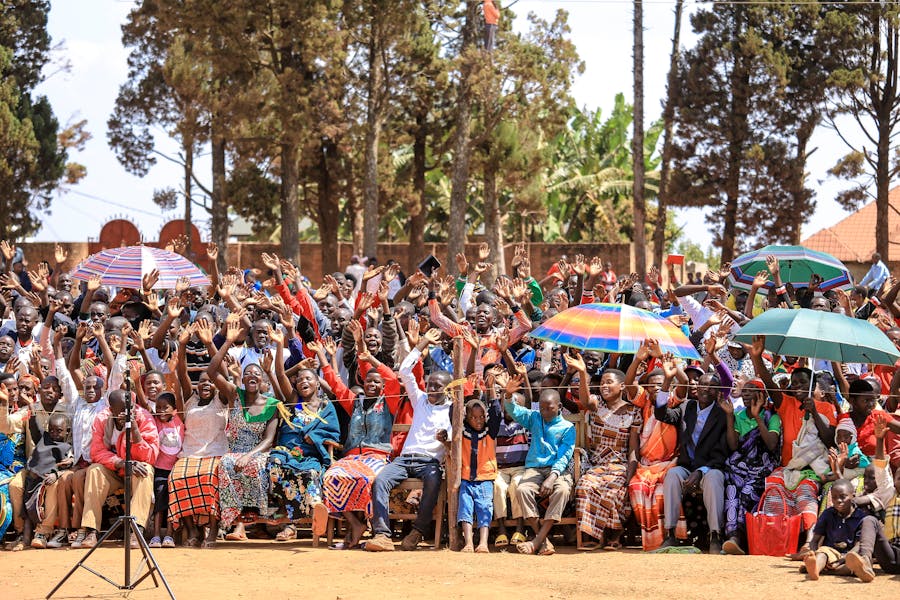
Africa is home to various countries with unique demographics, cultures, and histories. Among these nations, Nigeria is the largest country in Africa by population. With over 220 million residents, Nigeria’s growing population defines its global and regional significance. This West African nation has emerged as a cultural and economic giant, influencing the continent profoundly.
Population size is more than a mere statistic—it reflects a country’s dynamism, diversity, and potential. Nigeria’s large population creates opportunities for innovation, entrepreneurship, and cultural richness but also brings challenges, such as managing infrastructure and ensuring sustainable development. With cities like Lagos and Abuja thriving as hubs of commerce and culture, Nigeria’s population growth is a testament to its resilience and ambition.
This article explores why Nigeria is the largest country in Africa by population, exploring its demographic trends, historical growth, economic opportunities, and the implications of its size on regional and global affairs. Whether you’re curious about its cultural vibrancy or its role as a leader in Africa, this analysis provides a comprehensive view of what makes Nigeria a standout nation.
Largest Country in Africa by Population
Nigeria is the largest country in Africa by population, with over 220 million people. High fertility rates, youthful demographics, and urbanization drive its population growth. Nigeria’s cultural diversity, economic potential, and regional influence make it a pivotal nation on the African continent.
Why Is Nigeria the Largest Country in Africa by Population?
Nigeria’s title as the largest country in Africa by population is rooted in its unique combination of historical, geographical, and social factors. Its location as a gateway between West Africa and the Atlantic coast made it a hub for trade, migration, and settlement. These interactions, dating back centuries, established Nigeria as a densely populated and culturally diverse nation.
The nation’s high fertility rate primarily drives its population growth. Nigerian women have an average of 5.2 children, far exceeding global averages. This trend is supported by cultural and social norms that value large families. Advances in healthcare over the decades have also contributed to lower mortality rates, allowing more children to survive into adulthood.
Nigeria’s youthful demographic is another defining feature. Over 60% of Nigerians are under the age of 25, making it one of the youngest populations in the world. This vibrant, energetic workforce holds the potential to drive innovation, entrepreneurship, and economic growth, although it also presents challenges in education and employment.
Urbanization plays a critical role in Nigeria’s growth story. Cities like Lagos, Kano, and Abuja are expanding rapidly as people move from rural areas to urban centers in search of better opportunities. Lagos, in particular, is a megacity with over 20 million residents, known for its bustling economy, cultural scene, and entrepreneurial spirit.
Additionally, Nigeria’s population is bolstered by its cultural diversity. With over 250 ethnic groups and languages, the nation is a melting pot of traditions and heritage. This diversity enriches its culture and contributes to its global influence, particularly through the success of Nollywood films, Afrobeats music, and Nigerian literature.
What Drives Nigeria’s Rapid Population Growth?
High Fertility Rates
Nigeria’s fertility rate of approximately 5.2 children per woman significantly contributes to its rapid population growth. Cultural values favoring large families and limited access to contraception in rural areas sustain this trend. Unlike many developed nations with declining fertility rates, Nigeria’s remains robust, ensuring steady growth.
Declining Mortality Rates
Improvements in healthcare have reduced infant mortality and increased life expectancy. Vaccination programs, better access to medical facilities, and public health initiatives have allowed more children to survive into adulthood, further accelerating population growth.
Urbanization Trends
Rapid urbanization is reshaping Nigeria. Cities like Lagos, Abuja, and Port Harcourt absorb millions of rural migrants annually, fueling population growth in these urban hubs. Urbanization also boosts economic activity, with cities acting as centers for innovation and investment.
Migration and Internal Diversity
Nigeria attracts migrants from neighboring countries due to its economic opportunities and regional prominence. Additionally, internal migration between rural and urban areas enhances population density in key regions.
Youthful Demographics
With a median age of 18 years, Nigeria has one of the youngest populations globally. This youthful population creates challenges, such as the need for education and jobs, and opportunities, particularly for innovation and entrepreneurship.
Challenges of Being the Largest Country in Africa by Population
Infrastructure Deficit: Rapid population growth strains existing infrastructure, including roads, housing, water supply, and electricity. Urban areas, particularly Lagos, face severe traffic congestion, inadequate housing, and frequent power outages.
Unemployment and Underemployment: While Nigeria’s youthful population is an asset, high unemployment rates pose significant challenges. Many young Nigerians struggle to find jobs, leading to economic stagnation and social unrest.
Healthcare Access: A growing population increases the demand for healthcare services. Many rural areas lack adequate medical facilities and patient demand often overwhelms urban hospitals.
Educational Strain: Nigeria’s education system is pressured to accommodate millions of children and young adults. Insufficient schools, limited teacher training, and inadequate resources hinder educational progress.
Environmental Concerns: Population growth exacerbates deforestation, pollution, and waste management issues. Rapid urbanization also contributes to challenges such as flooding and the loss of arable land.
How Does Nigeria’s Population Fuel Its Economy?
Nigeria’s population is both a challenge and a boon for its economy. As the largest country in Africa by population, its massive domestic market is a magnet for investors, creating opportunities in industries ranging from technology to consumer goods. Key economic contributions include:
Agriculture
Despite urbanization, agriculture remains the backbone of Nigeria’s economy, employing over 35% of the workforce. Crops like cassava, yams, and maize are staples, while exports such as cocoa and palm oil contribute to foreign exchange earnings.
Technology and Innovation
Nigeria is a leader in Africa’s tech scene, with Lagos as a startup hub. Fintech, e-commerce, and app development companies cater to a tech-savvy, young population.
Entertainment Industry
Nollywood, the second-largest film industry globally, and Afrobeats music, led by stars like Burna Boy and Wizkid, highlight Nigeria’s cultural export power. These industries create jobs and enhance Nigeria’s global reputation.
Consumer Market
A population exceeding 220 million drives demand for consumer goods, from food and beverages to smartphones and automobiles. Multinational companies are increasingly targeting Nigeria as a key growth market.
Global Implications of Nigeria’s Population Growth
Regional Leadership: Nigeria’s population size translates to significant political and economic influence within Africa. It plays a central role in the African Union and regional bodies like ECOWAS, driving policies that affect the continent.
Cultural Influence: Nigeria’s cultural exports shape global perceptions of Africa. Nollywood films, Afrobeats music, and Nigerian literature are celebrated worldwide, enhancing the country’s soft power.
Migration Trends: Nigeria influences migration flows as a population leader. While many Nigerians seek opportunities abroad, particularly in Europe and North America, others contribute to regional economic activity within West Africa.
Investment Opportunities: International businesses view Nigeria’s population as a lucrative market. High demand benefits sectors such as telecommunications, real estate, and consumer goods.
Sustainability Challenges: Nigeria’s population growth highlights global issues like urbanization, resource allocation, and climate change, making it a focal point for sustainable development discussions.
Bottom Line
Nigeria’s status as the largest country in Africa by population underscores its significance on the continent and beyond. Its youthful, dynamic, growing population drives innovation, cultural influence, and economic potential. However, this growth also presents challenges, from infrastructure development to environmental sustainability.
Nigeria’s role as an African leader will only strengthen as it continues to evolve. Addressing its challenges while leveraging its opportunities will be key to ensuring that its population remains a valuable asset for the nation and the continent as a whole.
FAQ’s
Q: What is the largest country in Africa by population?
A: With over 220 million residents, Nigeria holds the title of the largest country in Africa by population.
Q: Why is Nigeria’s population growing so rapidly?
A: High fertility rates, urbanization, declining mortality, and a youthful demographic contribute to Nigeria’s rapid population growth.
Q: How does Nigeria’s population affect its economy?
A: Nigeria’s large population drives domestic demand, supports industries like technology and entertainment, and attracts international investment.
Q: What challenges does Nigeria face as Africa’s most populous country?
A: Challenges include infrastructure strain, unemployment, healthcare access, educational needs, and environmental concerns.
Q: How does Nigeria influence Africa and the world?
A: Nigeria’s population size, cultural exports, and economic potential make it a regional leader and a significant player on the global stage.