South Africa, a nation celebrated for its diverse landscapes and abundant natural resources, stands at a critical crossroads due to the increasing effects of climate change. As global temperatures rise and weather patterns grow more unpredictable, South Africa’s economy faces profound disruptions. From its agricultural backbone to its energy grid and iconic tourism sector, climate change reshapes every facet of economic life. While the challenges are significant, they also present an opportunity to innovate, adapt, and transition to a more sustainable future. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of climate change on South Africa’s economy, exploring key affected sectors, adaptation strategies, and the steps needed to build resilience.
The Impact of Climate Change on the Economy of South Africa
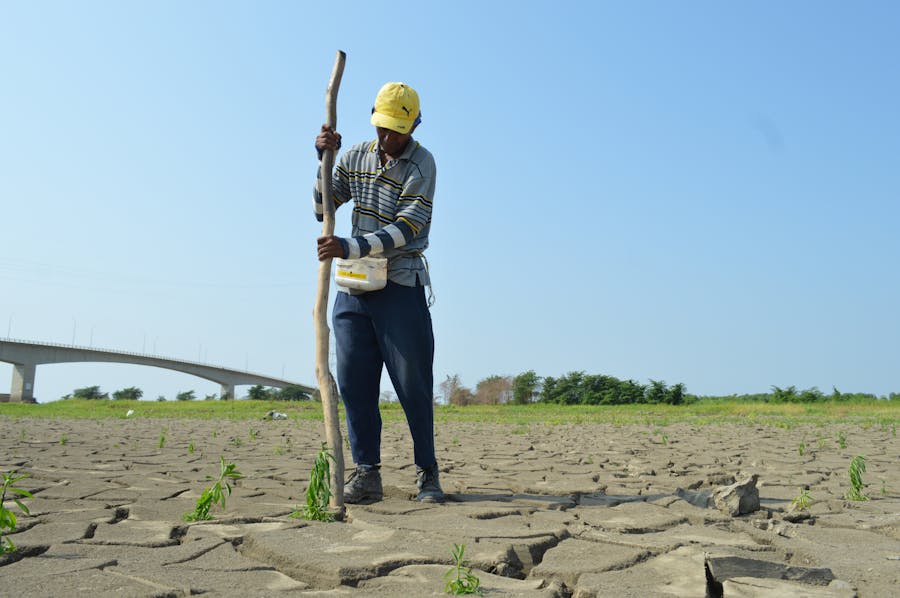
The impact of climate change on South Africa’s economy is far-reaching. Agriculture faces declining yields due to drought and erratic rainfall, threatening food security and export revenues. The energy sector needs help with water scarcity, which is affecting coal and hydropower generation. Tourism, a key GDP contributor, suffers from habitat loss, coastal erosion, and unpredictable weather, reducing its appeal. Climate-related illnesses strain healthcare systems, increasing public expenditure. These challenges highlight the urgent need for sustainable energy, agriculture, and infrastructure reforms.
Why Is Climate Change a Critical Economic Issue for South Africa?
Climate change has emerged as a defining issue for South Africa, threatening its economic stability and growth prospects. The problem lies not only in environmental degradation but also in the cascading economic effects across sectors.
Climate change affects South Africa’s agriculture, tourism, and infrastructure—the pillars of its economy. Frequent droughts, changing rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events disrupt agricultural productivity. Once a robust contributor to the GDP, tourism is at risk due to habitat destruction and declining biodiversity. Energy generation faces water scarcity, particularly for coal-fired plants requiring significant water resources. Moreover, the cost of rebuilding infrastructure damaged by floods or maintaining healthcare services for climate-related illnesses further strains the economy.
South Africa’s reliance on coal for energy exacerbates its vulnerability. As global pressure to reduce carbon emissions intensifies, the country risks losing foreign investments unless it transitions to greener energy sources. Addressing climate change is an environmental necessity and an economic imperative for South Africa to remain competitive globally.
How Does Climate Change Impact South Africa’s Agricultural Sector?
The Agricultural Backbone
Agriculture is crucial in South Africa’s economy, contributing significantly to employment and GDP. However, climate change threatens this backbone through water shortages, declining soil fertility, and pest outbreaks.
Droughts and Food Security
Prolonged droughts have become common, with water scarcity reducing irrigation capabilities. Staple crops like maize, wheat, and sorghum suffer lower yields, directly impacting food security and export revenues. The economic losses from droughts also extend to livestock farming, with herders struggling to provide adequate water and grazing land.
Economic Ripple Effects
The effects on agriculture go beyond food supply. Rising food prices due to reduced yields contribute to inflation, making essentials unaffordable for low-income families. Smallholder farmers face financial instability, pushing rural communities into deeper poverty. The loss of agricultural exports weakens the national trade balance, affecting overall economic growth.
Adaptation as a Solution
Efforts like adopting drought-resistant crops, improving irrigation efficiency, and promoting sustainable farming offer hope. However, these require substantial investment and policy support, which South Africa still needs to be grappling to implement effectively.
What Are the Effects of Climate Change on South Africa’s Energy Sector?
The energy sector is another critical area where climate change’s impact is glaring. South Africa’s dependency on coal-fired power plants poses significant challenges due to water scarcity and extreme weather events.
- Water Dependency in Energy Production
Coal-fired power plants rely heavily on water for cooling, making them vulnerable during droughts. Hydropower, another renewable source, also suffers from declining water availability, leading to frequent power outages that disrupt businesses and economic activity. - Rising Demand for Cooling Systems
As temperatures rise, the demand for cooling systems increases, placing additional pressure on an already fragile electricity grid. Load shedding—a common occurrence in South Africa—exacerbates the economic fallout by slowing industrial production and reducing consumer spending. - Transitioning to Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind offer a way forward. However, the transition requires massive infrastructure investments and policy shifts to reduce the country’s reliance on coal. Although efforts like the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme (REIPPPP) are steps in the right direction, their implementation has been slow.
Why Is Tourism Vulnerable to Climate Change?
Tourism is one of South Africa’s most vibrant economic sectors, attracting millions of visitors annually to its wildlife reserves, beaches, and cultural sites. However, climate change threatens this industry in several ways.
- Wildlife and Habitat Loss
Iconic species like rhinos, lions, and elephants face shrinking habitats due to rising temperatures and deforestation. As biodiversity declines, eco-tourism—a significant draw for international visitors—loses its appeal. - Coastal Challenges
Rising sea levels and coastal erosion damage beaches, hotels, and resorts. South Africa’s coastline, particularly areas like Cape Town, faces significant risks, which deter tourists and increase repair costs. - Unpredictable Weather Patterns
Erratic weather makes travel planning challenging for tourists, reducing the influx of international visitors. The overall decline in tourism revenues affects local economies that are reliant on this sector.
How Does Climate Change Strain Healthcare and Infrastructure?
Healthcare Burden: Climate change introduces new health challenges, including heat-related illnesses, pollution-related respiratory issues, and the spread of vector-borne diseases like malaria. These challenges strain healthcare systems, requiring additional resources for prevention and treatment.
Infrastructure Maintenance: Frequent floods and extreme weather damage roads, bridges, and public utilities, increasing repair and maintenance costs. Urban areas are particularly vulnerable, with unplanned settlements facing the brunt of climate-related disasters.
What Are the Strategies for Mitigating Economic Impacts?
South Africa has a range of options to address the economic impacts of climate change:
- Investing in Renewable Energy: Solar and wind power can reduce reliance on coal, lower emissions, and create green jobs.
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Introducing better irrigation techniques and drought-resistant crops can stabilize food production.
- Building Resilient Infrastructure: Upgrading roads and buildings to withstand floods and extreme temperatures minimizes economic losses.
- Public Awareness and Education: Empowering communities with knowledge on climate adaptation fosters collective resilience.
Final Word
The impact of climate change on South Africa’s economy is undeniable, affecting key sectors like agriculture, energy, and tourism. These challenges demand urgent action to build resilience and ensure long-term economic stability. By investing in renewable energy, adopting sustainable farming practices, and improving infrastructure, South Africa can mitigate the adverse effects of climate change. Addressing these issues requires government, businesses, and citizens collaborative efforts to create a sustainable and prosperous future.
FAQ’s
Q: How does climate change affect South Africa’s economy?
A: Climate change disrupts agriculture, energy production, and tourism, increasing healthcare costs and requiring significant investments in infrastructure repairs.
Q: What sectors are most vulnerable to climate change in South Africa?
A: Agriculture, energy, tourism, and healthcare are the most affected sectors, with cascading effects on food security, employment, and public spending.
Q: How can South Africa combat the economic effects of climate change?
A: Investing in renewable energy, promoting sustainable agriculture, and building climate-resilient infrastructure are key strategies for mitigating impacts.
Q: Why is renewable energy critical for South Africa?
A: Renewable energy reduces dependence on coal, lowers emissions, and offers economic benefits through job creation and energy security.
Q: What role does tourism play in South Africa’s economy amidst climate change?
A: Tourism is a significant contributor to the GDP but faces risks from habitat loss, coastal erosion, and erratic weather patterns, which reduce its appeal to visitors.